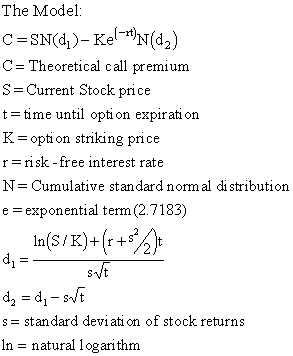
An alternative calculation of the Black Scholes formula for effective hedging programmes - The Global Treasurer

Different approach to Black Scholes model and validation of dynamic delta hedging with Monte Carlo simulation - The Global Treasurer

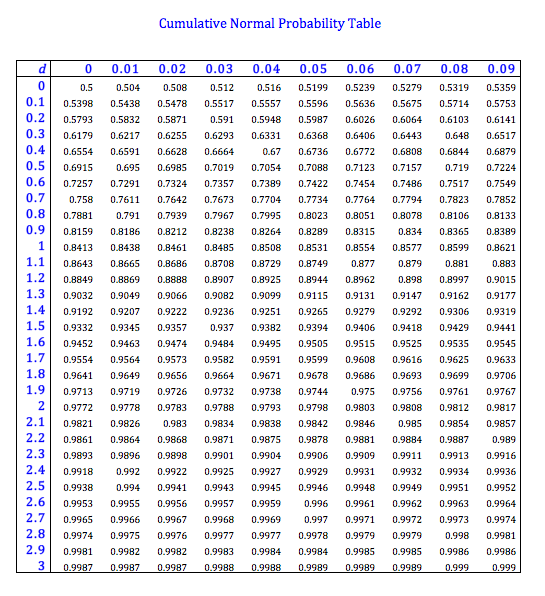
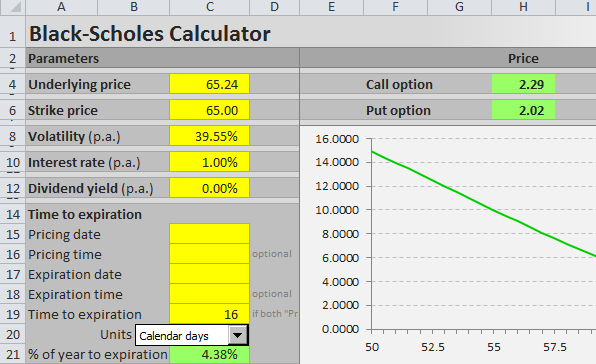
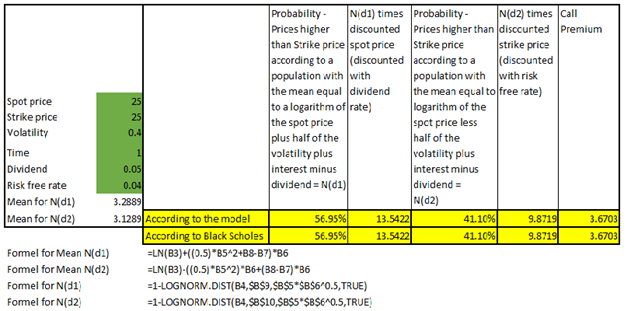
In the black scholes formula how can N(d1) represent the expected return in the event of an exercise and at the same time also mean 'delta' - probability that the option will
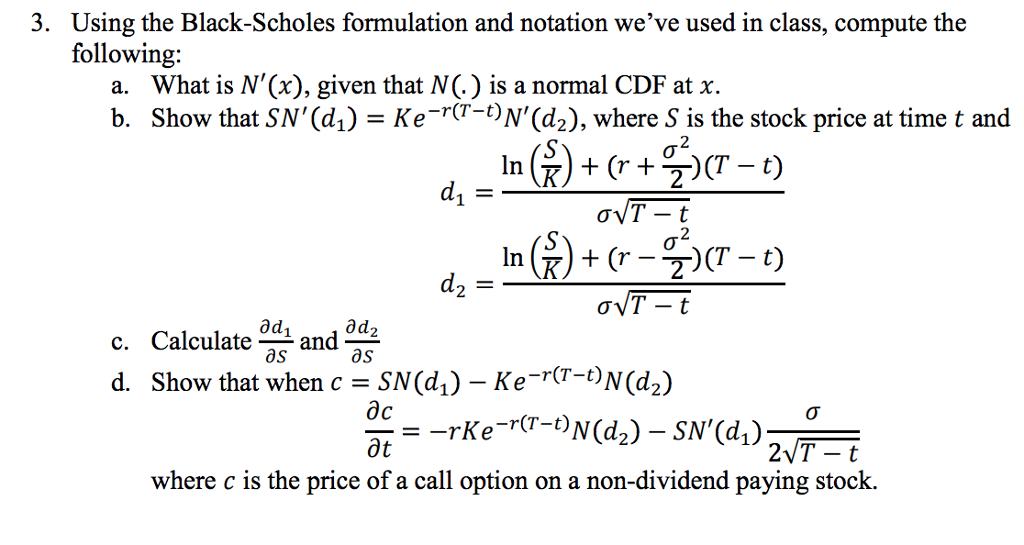
Lecture 12: The Black-Scholes Model Steven Skiena Department of Computer Science State University of New York Stony Brook, NY 11